Standardizing Predicted Body Weight Equations for Mechanical Ventilation Tidal Volume Settings.
Standardizing Predicted Body Weight Equations for Mechanical Ventilation Tidal Volume Settings.
Linares-Perdomo O, East TD, Brower R, Morris AH.
Chest. 2015 Mar 5. 14-2843
用标准化理想体重公式设置机械通气潮气量
徐晓婷摘译
背景:对于肺保护性机械通气策略,最新的指南建议是按6ml/kg的理想体重来估算潮气量的。对于研究和病人来说,不同的理想体重计算公式会给潮气量的计算带来重要的不同。
BACKGROUND:
Recent recommendations for lung protective mechanical ventilation (MV) include a tidal volume (VT) target of 6 ml/kg predicted bodyweight (PBW). Different PBW equations might introduce important differences in tidal volumes delivered to research subjects andto patients.
方法:理想体重公式利用体重/年龄/性别作为输入变量。我们比较了在临床实验中使用的涵盖生理范围内的年龄和身高的计算公式:NIH ARDS Network (ARDSNet), actuarial table (ACTUARIAL), 和 Stewart(STEWART)方程,用三维和二维的表面分析来比较这些理想体重方程。然后我们用实际临床受试者的年龄身高指标来量化理想体重方程之间的差异。
METHODS:
PBW equations use height, age, and gender as inputvariables. We compared NIH ARDS Network (ARDSNet), actuarial table (ACTUARIAL),and Stewart (STEWART) PBW equations used in clinical trials, acrossphysiologic ranges for age and height. We used 3-D and 2-D surface analysis tocompare these PBW equations. We then used age and height from actual clinical trialsubjects to quantify PBW equation differences.
结果:不同的理想体重公式中存在着明显而又潜在的区别。ACTUARIAL和ARDSNet两种方法在女性身上的表现各有千秋。ACTUARIAL和ARDSNet两种理想体重公式在年龄和升高上超过30%的女性以及24%的男性身上有统计学上的差异。STEWART和ARDSNet两种理想体重公式相比是25%和15%。年老和个子矮的对象,尤其是女性会有巨大的数字上的差异。临床试验中实际的差别在男性高达15%,女性高达24%。
RESULTS:
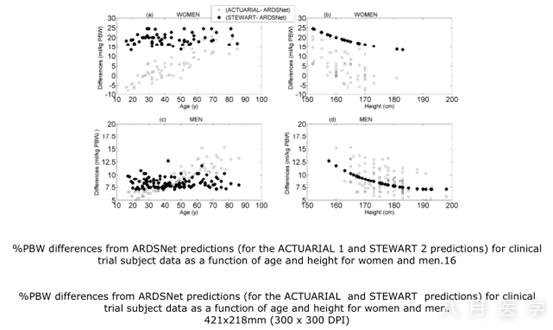
Significant potential differences existbetween these PBW predictions. The ACTUARIAL and ARDSNet surfaces for womenwere the only surfaces that intersected and produced both positive and negativedifferences. Mathematical differences between PBW equations at limits of height and age exceeded 30%in women and 24% in men for ACTUARIAL versus ARDSNet, and about 25% for womenand 15% for men for STEWART versus ARDSNet. The largest mathematicaldifferences were present in older, shorter subjects, especially women. Actualdifferences for clinical trial subjects were as high as 15% for men and 24% forwomen.
结论:不同理想体重公式计算潮气量的明显差异可能是不同研究间差异的原因。不同的研究应当采用同样的理想体重公式标准。我们推荐使用ARDSNet的理想体重公式,因为它为确定6ml/kg的理想体重提供了一个适当的目标。
CONCLUSIONS:
Significant differences between PBW equations for both men and women could be importantsources of inter-study variation. Studies should adopt a standard PBW equation.We recommend using the NIH/NHLBI ARDS Network PBW equation because it isassociated with the clinical trial that identified 6ml/kg PBW as an appropriatetarget.

Figure 1
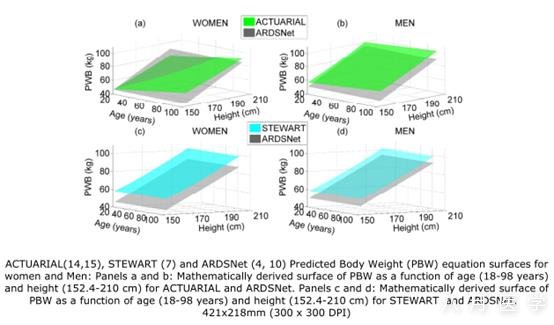
Figure 2
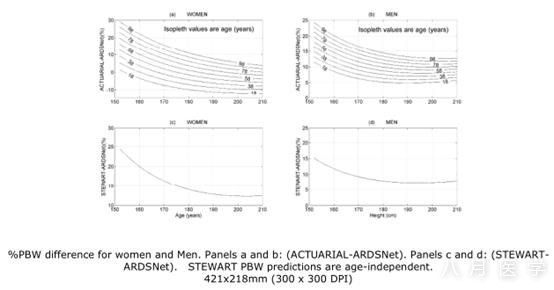
Figure 3